Caffeine Side Effects
– 10 Side Effects of Too Much Caffeine –
What kind of drink did you have this morning?
The vast majority of us will either answer a cup of coffee or tea.
Both are one of the most consumed beverages in the world. There are many reasons why coffee or tea has become such an essential part of our daily lives.
For once, coffee and tea are incredibly healthy. It also doesn’t hurt that both are delicious in all of its very colorful and creative flavor profiles as well.
On top, especially coffee and tea give us energy to navigate more efficiently through our days. This is also thanks to one of the drinks’ key ingredients, namely caffeine.
Most coffee and tea types contain high amounts of caffeine.
It is a very useful substance that may boost your mood. And, caffeine helps to enhance your metabolism, as well as mental and physical performance.
In a low to moderate and regular consumption, studies show that caffeine is safe for most people. There is no real concern unless you would consume too much caffeine in a short period of time.
High doses of caffeine may lead to unpleasant or even dangerous side effects.
Additionally, research shows that our genes have a great influence on our tolerance to it. Not every person is reacting or experiencing the same degree of symptoms.
Some consumers can easily tolerate more caffeine than others. Whereas, others may encounter more severe effects in a negative way.
What are these potential caffeine side effects?
Here are the 10 most common side effects of too much caffeine.
-
Tiredness by Too Much Caffeine
Caffeinated beverages like coffee and tea are known to boost energy levels.
However, by consuming too much caffeine these drinks can also lead to the opposite effect. After the caffeine eventually left your body. You might experience a so-called rebound fatigue.

As a result, you will even feel more tired and exhausted than before.
Health experts reviewed a total of 41 studies about caffeinated energy drinks. The overall outcome was that they of course increase our alertness. Additionally, energy drinks will also improve our mood for several consecutive hours.
However, the great majority of participants were often even more tired than usual, at the following day.
Of course, you there is one way to avoid this potential rebound effect. Consumers would just have to drink a lot more caffeine throughout the entire day.
With more continuous caffeine, you may further delay signs of tiredness. But at some point, you will probably even feel more exhausted.
Your body might just give in then. Potentially, it might completely collapse and shut down over a period of time.
In addition, too much caffeine per day can even lead to other side effects. We will discuss many of them in this article.
Coming back to tiredness, a caffeine overdose may affect your ability to sleep at night then.
You might have serious difficulties to fall asleep in the first place. Hence, the next day can become even more exhausting then.
Many of us already experienced sleepless nights and the effects after.
In general, it is best to consume caffeine rather in moderate than high doses.
This way, you can actually best maximize the caffeine’s benefits on your energy and overall productivity.
-
Addiction
Caffeine, as a stimulant, does have many health benefits.
But there can also be no denying to a very important fact. Indeed, the stimulant can also become habit-forming, hence potentially addictive.

Several detailed reviews claim that caffeine triggers certain brain chemicals. These chemicals will be influenced in the same way such as cocaine and amphetamines then, for example.
However, caffeine does not cause classic addiction same as these drugs do.
Nonetheless, there are still potential addictive risk factors. Too much caffeine can lead to psychological or physical dependency.
Your mind and body might develop a certain reaction of craving to it. This is especially the case at high dosages.
There is one interesting case study with people, who usually consumed high dosages. Other participants of the same study maybe just had a moderate or no caffeine intake at all.
All of these participants took part in a basic word test. This test took place after going without caffeine for one night.
Most participants did fine and had no problem completing the test. Only high regular caffeine consumers showed signs of craving. Any coffee-related words in that test made them long for caffeine.
As conclusion, experts suggest that the frequency of caffeine intake seems to play a role in our overall dependency towards it.
Furthermore, another study showed similar results. Over 200 regular caffeine consumers had to complete a questionnaire here.
Again, this took place after a longer time without caffeine, namely a total of 16 hours.
During the questionnaire, many users complained about increasing headaches. They also experienced increasing fatigue, besides other withdrawal symptoms compared to non-daily users.
Where does this leave us?
Indeed, caffeine may not cause true addiction.
However, regular, excessive consumers are likely to become more dependent on some of its caffeine side effects.
-
Anxiety by Caffeine Side Effects
Caffeine may increase overall alertness.

In order to achieve this, the compound particularly blocks the effect of adenosine. It is a brain chemical that normally makes us feel tired.
Simultaneously, adenosine also triggers the release of adrenaline. In very short terms, adrenaline is our survival hormone.
Under any potentially threatening situations, it helps us to be fast or strong. Adrenaline triggers certain physiological changes in our body.
This makes our heart rush oxygenated blood to our muscles, even before we react or have mentally chosen a course of action already.
This natural instinct and related chemical reaction ensured our humane survival for all of this time being.
However, at higher adrenaline doses, these increased energy effects can become too exaggerated. They may lead to anxiety and nervousness instead.
In particular, extremely high daily intakes of 1.000 mg or more per day are reported causing particular caffeine side effects. These would be nervousness, jitteriness and similar symptoms in most people.
Furthermore, also moderate doses may cause rapid breathing. And, it can increase stress levels, especially if you consume everything within one sitting.
Interestingly, the majority of stress level results are similar between regular and less frequent consumers. This suggests that the compound more or less has the same effect.
It does not necessarily matter, if you drink regularly or not. The effect may remain the same per each consumption time.
Nevertheless, all of these results and effects are high variable. For instance, the coffee’s caffeine content can very much vary from type to type. Generally, 2 to 4 cups of coffee are not a real problem for the average person.
Nonetheless, in case you notice or feel nervous or jittery. Please consider to cut back on your caffeine intake.
-
High Blood Pressure by Too Much Caffeine
Typically, caffeine does not necessarily increase the risk of heart disease or stroke in most people.
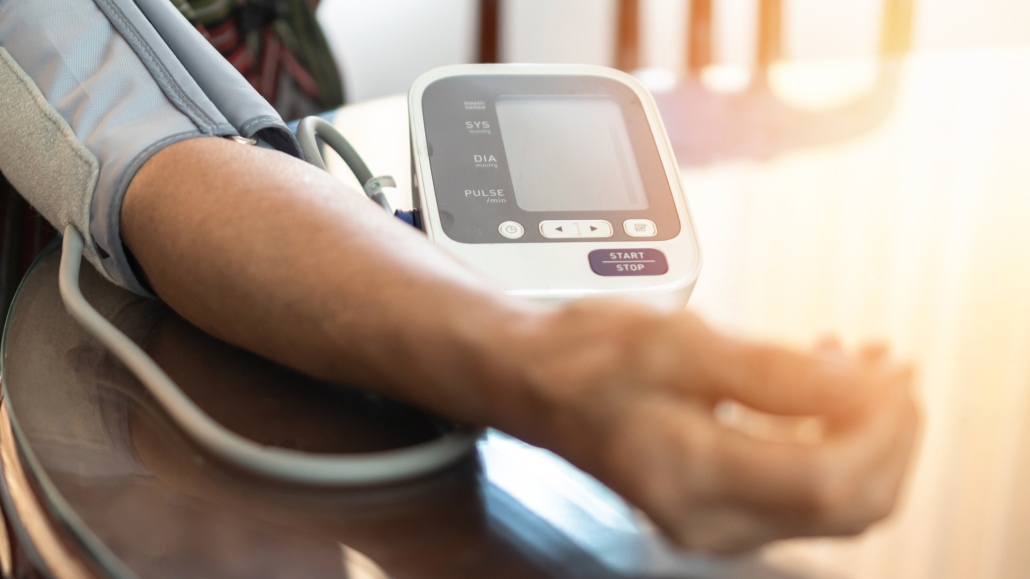

However, several studies indicate that it may raise blood pressure. This is mainly due to its stimulatory effect on our nervous system.
Higher blood pressure can potentially become a risk factor for heart attack and stroke. It may damage our blood arteries over time.
As a result, the blood flow to our heart and brain may be restricted. Our bloodstream might not sufficiently supply these organs anymore.
Luckily, caffeine side effects on our blood pressure are merely temporary. They tend to fade away over a period of time.
Furthermore, non-regular caffeine consumers usually seem to experience the strongest impact of any effects.
But even entirely healthy people should rather be moderate with their regular caffeine intake. High caffeine intake can also raise blood pressure during exercise for them as well.
Therefore, please keep the right amount of dosage and timing of caffeine in mind. Especially in case you ae experiencing high blood pressure already.
-
Digestive Issues by Caffeine Side Effects
Most people appreciate their morning cup of coffee out of a variety of great reasons.
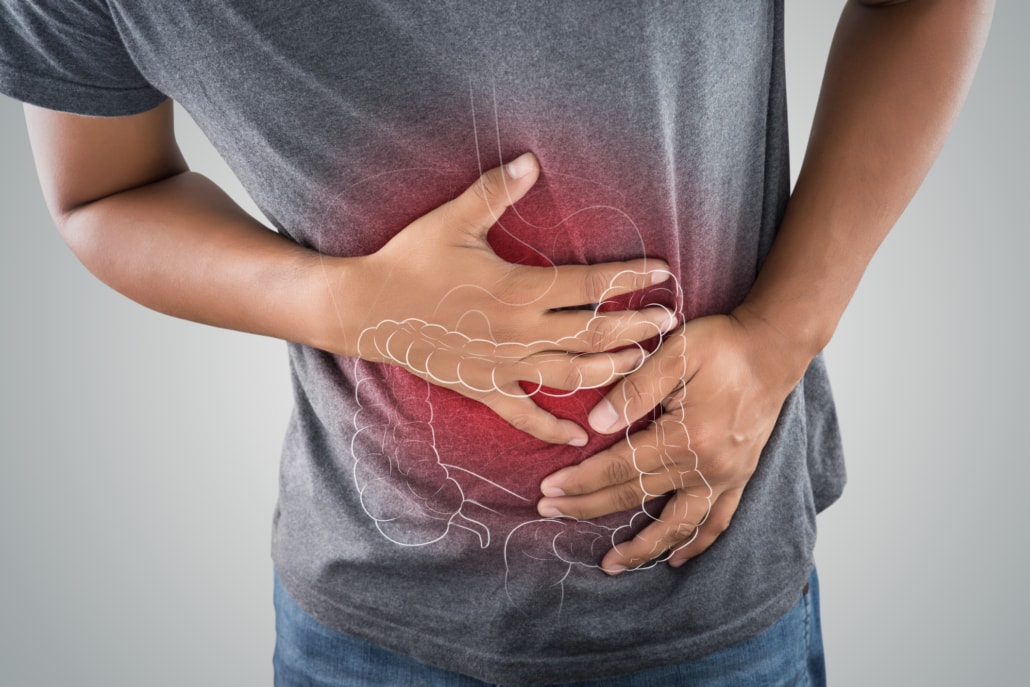
For instance, many drinkers find it beneficial that it helps getting their bowels moving. Your morning visit at the toilet will simply be more relaxed and less stressful then.
Coffee is long-known for its laxative effect already. It helps releasing the hormone gastrin. Our stomach produces it to speed up activity in the colon.
Quite fascinatingly, even decaffeinated coffee can trigger a similar response and effect in our body.
In addition, also the coffee’s caffeine seems to stimulate bowel movements. It specifically increases the peristalsis. The peristalsis is basically the movement that transfers food through our digestive tracts.
This movement happens in wave-like muscle contractions.
Too much caffeine can however potentially loosen up the muscle movements more severely. Loose stools can be the result or even diarrhea in some people.
Furthermore, larger amounts of caffeine may also worsen the gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) for some people. Experts speak of GERD when stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach.
However, scientists still need to further research in this area. Studies sizes are only very small at the moment. It is still too early for final assumptions.
Nonetheless, coffee and its caffeine can potentially have major effects on our digestive system.
You should consider cutting back your amount. If you experience any of these caffeine side effects.
-
Infertility in Women by Too Much Caffeine
Does caffeine lower the chances of getting pregnant?
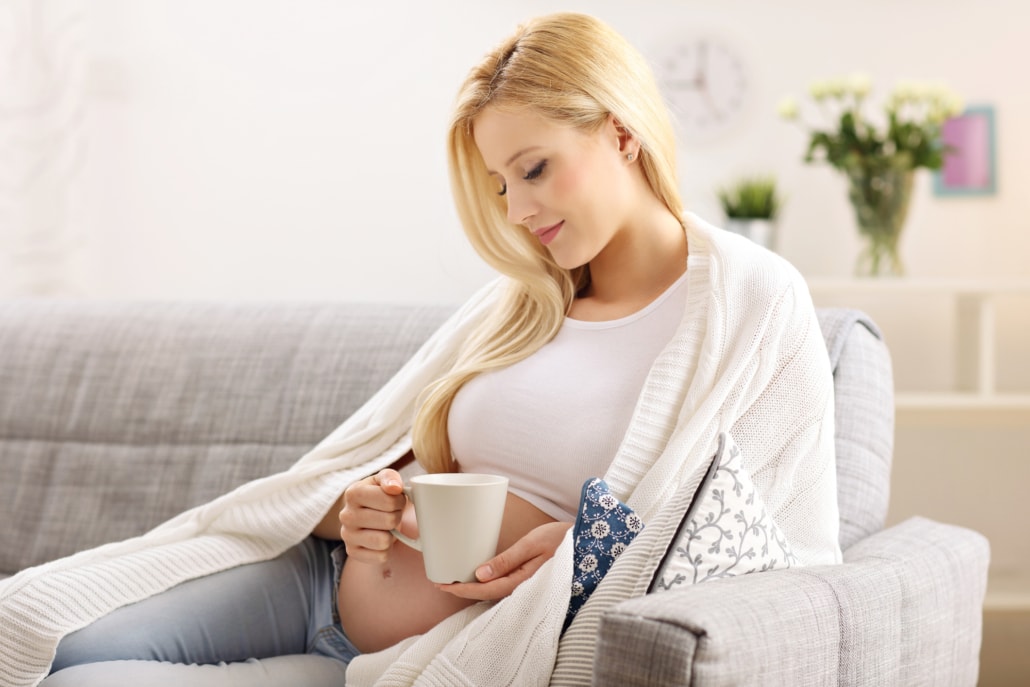

The question alone may raise concerns in many of us already.
To some degree, the answer is yes. Indeed, research suggests that caffeine may affect human fertility.
This especially applies to women, who regularly drink coffee or energy drinks in higher amounts.
A quite recent study shows that caffeine may interfere with the muscular contractions of the fallopian tubes then.
These tubes are especially responsible for successfully moving the egg from the ovary to the uterus. The corresponding conceptions naturally take place in the fallopian tubes as well then.
In simpler terms, a successful fertilization of the egg will become harder with higher caffeine amounts.
Too much caffeine reduces the smooth muscle contractions in the fallopian tubes. The egg may not reach its most optimal area or location for conception.
Therefore, women who are trying to get pregnant should not consume caffeine at all.
Or, they at least have caffeine in much lower and more moderate amounts. Most experts agree on 200 mg or less per day.
It tremendously lowers the risk of not successfully developing a fetus. As a result, chances of getting pregnant are increasing again.
For more details or advice, please continue reading here.
-
Insomnia
One of the most appreciated qualities of caffeine is its ability to help people staying awake.
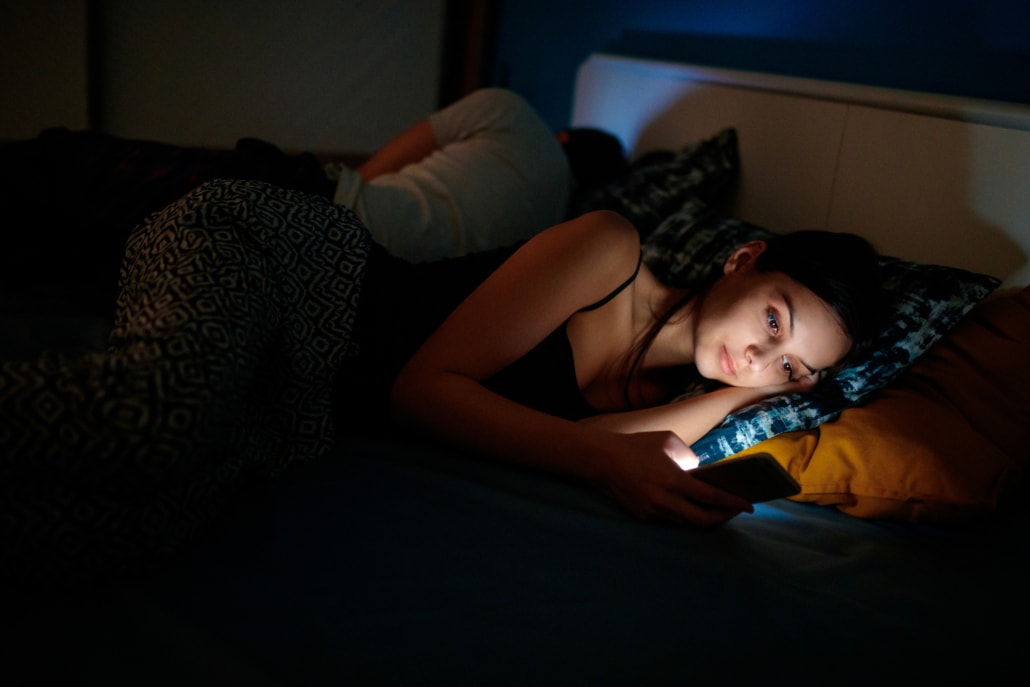

However, too much caffeine can lead to the exact opposite. You might have difficulties to get enough rest and sleep.
Several studies show that higher caffeine intakes increase the time of falling asleep. It just takes longer for us to really find rest, mentally and physically.
Additionally, people may not just fall asleep later but also sleep less in total. An average adult needs between 7 to 9 hours of sleep per nights. Anything below can cause various further stress factors.
By contrast, lower caffeine amounts don’t seem to affect our sleep habits very much. Only if you are a ‘light sleeper’, you might still experience difficulties, even then.
In general, caffeine side effects such as insomnia also depend on our own genetics and other factors.
Furthermore, if you consume caffeine later in the day, it may interfere with your regular sleep patterns even more. Because, its effects can take several hours to wear off again.
Your entire, usual sleep routine may be out of balance then.
Studies indicate that caffeine remains in your system for an average of 5 hours. However, depending on every individual, the actual time period may range from 1.5 to even 9 hours.
In addition, further research has revealed some practical suggestions for us.
It is best to cut off our caffeine consumption by the early afternoon the latest. This will then optimize your sleep later on.
Overall, it is important to pay attention two both the amount and timing of our caffeine consumption.
-
Muscle Breakdown by Caffeine Side Effects
People may also develop rhabdomyolysis, if they regularly consume large amounts of caffeine.
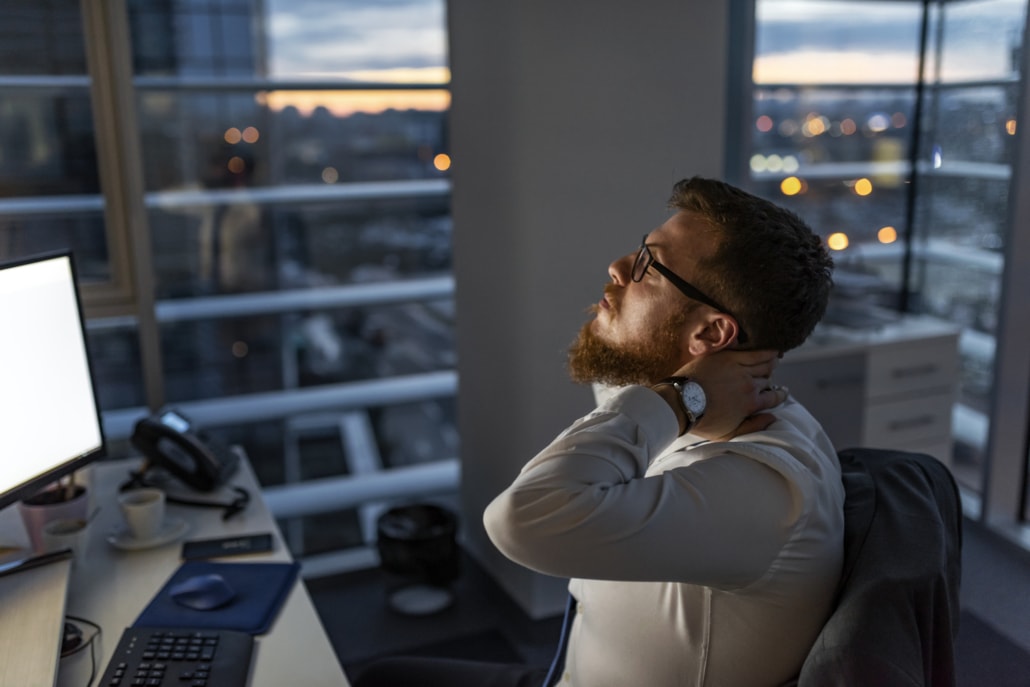

This very serious condition describes the breakdown of damaged skeletal muscle.
The muscle breakdown causes the release of myoglobin into our bloodstream. Myoglobin is a protein, which is responsible storing oxygen in our muscles.
However, in case you have too much myoglobin in your blood, a number of health risks can occur.
Unfortunately, very large dosages of caffeine can trigger rhabdomyolysis and its processes. Potential health risks include muscle weakness, low urine output, kidney damage and others.
It is important to note that most large amounts (over 600 mg of caffeine) would have to be consumed within a short period of time. Only then, health experts are expecting any of the diseases’ symptoms.
But, highly sensitive people might already experience first symptoms at lower amounts.
Any concerned people should therefore be more cautions.
How can we reduce the risk of rhabdomyolysis?
It is best to limit our consumption at around 250 mg of caffeine per day. If you are uncertain of your own tolerance level, this is the general, professional recommendation.
Furthermore, also more regular consumers can lower overall risks of any caffeine side effects at around 400 mg on a daily basis.
-
Rapid Heart Rate
The stimulant, caffeine, may make your heart beat faster.
As a temporary result and in more severe cases, the entire heartbeat rhythm can potentially change.
This phenomenon is called atrial fibrillation. Common symptoms often include heart palpitations, shortness of breath and weakness.
Scientific studies reported such cases in young people, for example. These participants mainly consumed energy drinks with extremely high dosages of caffeine.
Several young people showed changes of heart rhythms after.
However, not everyone seems to experience these effects. Indeed, other studies with people having particularly heart problems showed different results.
Many of them were able to tolerate large amounts of caffeine despite their pre-conditions.
Moreover, another study showcased something similar. 51 heart failure patients consumed 100 mg of caffeine per hour for a total of 5 hours.
None of them showed changes of higher heart rates and rhythms after.
Nonetheless, nobody should take this topic and its concerns too lightly. Because, there are currently several mixed study results.
Therefore, it is difficult to provide a clear answer and guideline as of now.
In general, it seems that these effects greatly vary from person to person.
However, if you feel any of them, please consider reducing your caffeine intake immediately.
-
Frequent Urination and Urgency
Last but certainly not least, one quite common caffeine side effect can be increased urination.
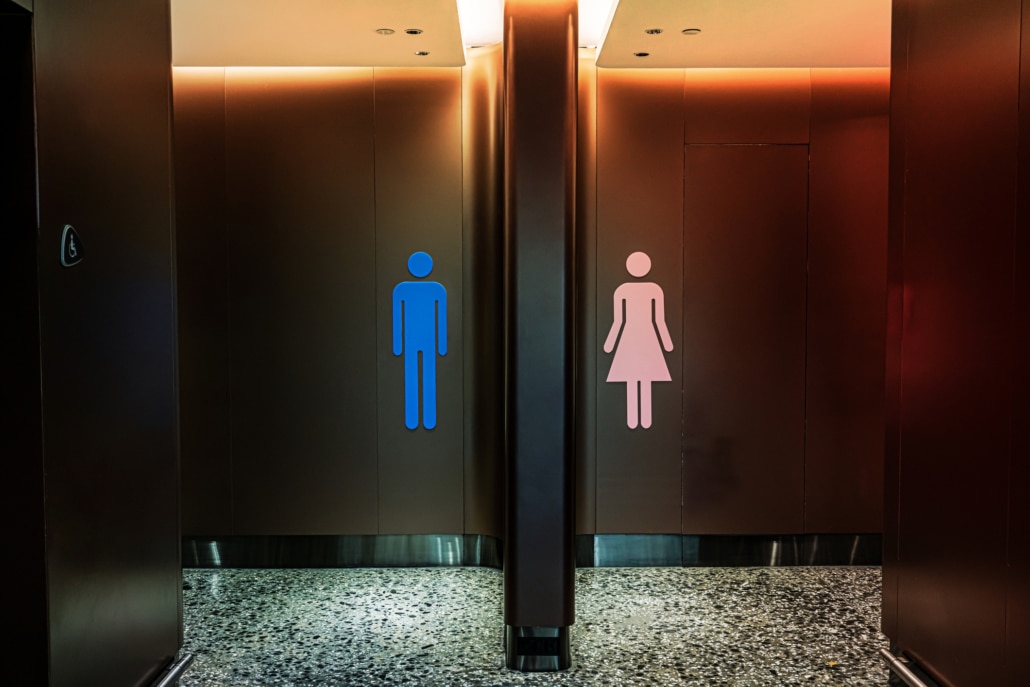

In fact, caffeine can potentially have stimulating effects on the bladder.
Let’s put it in very simple words. If you drink more coffee or tea than usual, you might have to go to the bathroom more often.
Concerning this issue, most research still mainly focuses on older people these days. This age group is likely the most being at imminent risk.
Additionally, health scientists also examine consumers with overactive bladders or incontinence in general.
Even further, some newer studies also finally researched first young to middle-aged people with overactive bladders, as well.
During these study cases, the participants consumed 2 mg of caffeine per pound (4.5 mg per kilogram) of their total body weight. This happened on daily basis over a longer period of time.
In total and on average, it would equate to 300 mg of caffeine per day, for a healthy person weighing around 150 pounds (68 kg).
When the results came in. They showed that the majority experienced significant increases in urinary frequency and urgency.
But this side effect does not only concern those with overactive bladders. Also healthier people may develop symptoms with too much caffeine.
Usually, people, who consume more 450 mg daily, can have significantly increased health risks.
What about you, actually? Are you normally drinking a lot of caffeinated beverages?
If you do and feel that your urination is more frequent or urgent than it should be. It might be a good idea to reduce your caffeine intake a bit.
Your symptoms may improve already then.
In case of more serious symptoms for any of the caffeine side effects, please go and see a doctor.
Final Thoughts on Caffeine Side Effects
I hope that this article and information didn’t scare you too much.
This was not the intention. It is rather to make you aware of any potential outcomes.
If you cannot limit your overall caffeine consumption, some of these caffeine side effects may occur.
However and in general, caffeine presents a lot more benefits than worrying side effects.
At the end of the day, it literally depends on us and our daily habits.
Light to moderate caffeine intake brings no problems. Anything above 400 mg of caffeine per day can already become critical for some people.
Younger people, pregnant women and people with certain pre-conditions should even be more cautious than others.
However and still then, any physical and mental responses to too much caffeine can vary from person to person.
Nonetheless and in general, the main reason and intention of consuming caffeine is its vast benefits. So, having a good rest and productive energy level is surely our main desire.
I am sure, we can all agree on this.
That is why many experts recommend against excessive caffeine consumptions, of course.
What do you think?
Have you maybe experienced any caffeine side effects already?
How much is possibly too much caffeine for you?
Feel free to share your experiences and thoughts with us.
Until then, stay safe, healthy and properly caffeinated.
Cheers!
Related Posts
 https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/What-is-Caffeine-–-Is-it-Good-or-Bad-for-Your-Health-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-04-25 11:19:442021-04-25 11:19:44What is Caffeine? – Is it Good or Bad for Your Health –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/What-is-Caffeine-–-Is-it-Good-or-Bad-for-Your-Health-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-04-25 11:19:442021-04-25 11:19:44What is Caffeine? – Is it Good or Bad for Your Health – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/How-Much-Caffeine-is-in-a-Cup-of-Coffee-All-You-Need-to-Know-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-04-25 11:10:082021-04-25 11:10:08How Much Caffeine is in a Cup of Coffee – All You Need to Know –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/How-Much-Caffeine-is-in-a-Cup-of-Coffee-All-You-Need-to-Know-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-04-25 11:10:082021-04-25 11:10:08How Much Caffeine is in a Cup of Coffee – All You Need to Know – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-and-Antioxidants-A-Complete-Overview-–-1.jpg
1413
2122
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-03-14 03:52:072021-03-14 03:52:07Coffee and Antioxidants – A Complete Overview –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-and-Antioxidants-A-Complete-Overview-–-1.jpg
1413
2122
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-03-14 03:52:072021-03-14 03:52:07Coffee and Antioxidants – A Complete Overview – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Overdose-–-A-Review-on-How-Much-is-Too-Much-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-03-14 03:44:312021-03-14 03:44:31Caffeine Overdose – A Review on How Much is Too Much –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Overdose-–-A-Review-on-How-Much-is-Too-Much-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-03-14 03:44:312021-03-14 03:44:31Caffeine Overdose – A Review on How Much is Too Much – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Lose-Weight-with-Coffee-–-Does-Coffee-Help-Burning-Fat-–-1.jpg
1412
2122
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-03-14 03:34:242021-03-14 03:34:24Lose Weight with Coffee – Does Coffee Help Burning Fat? –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Lose-Weight-with-Coffee-–-Does-Coffee-Help-Burning-Fat-–-1.jpg
1412
2122
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-03-14 03:34:242021-03-14 03:34:24Lose Weight with Coffee – Does Coffee Help Burning Fat? – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Natural-Coffee-Sweeteners-–-Best-Natural-Sugar-Substitutes-For-You-–-1.jpg
1502
1997
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-20 05:43:182021-03-03 07:41:19Natural Coffee Sweeteners – Best Natural Sugar Substitutes For You –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Natural-Coffee-Sweeteners-–-Best-Natural-Sugar-Substitutes-For-You-–-1.jpg
1502
1997
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-20 05:43:182021-03-03 07:41:19Natural Coffee Sweeteners – Best Natural Sugar Substitutes For You – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Great-Milk-Alternatives-–-Your-9-Best-Nondairy-Substitutes-for-Milk-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-20 05:26:492021-03-03 10:47:18Great Milk Alternatives – Your 9 Best Nondairy Substitutes for Milk –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Great-Milk-Alternatives-–-Your-9-Best-Nondairy-Substitutes-for-Milk-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-20 05:26:492021-03-03 10:47:18Great Milk Alternatives – Your 9 Best Nondairy Substitutes for Milk – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Make-Your-Coffee-Healthy-–-Best-10-Ways-For-A-Better-Coffee-Experience-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 08:13:182021-03-03 10:57:16Make Your Coffee Healthy – Best 10 Ways For A Better Coffee Experience –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Make-Your-Coffee-Healthy-–-Best-10-Ways-For-A-Better-Coffee-Experience-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 08:13:182021-03-03 10:57:16Make Your Coffee Healthy – Best 10 Ways For A Better Coffee Experience – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10-Best-Ways-to-Eat-Less-Sugar-–-How-to-Cut-Down-on-Sugar-–-1-scaled.jpg
1709
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 08:07:142021-03-03 10:58:4810 Best Ways to Eat Less Sugar – How to Cut Down on Sugar –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10-Best-Ways-to-Eat-Less-Sugar-–-How-to-Cut-Down-on-Sugar-–-1-scaled.jpg
1709
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 08:07:142021-03-03 10:58:4810 Best Ways to Eat Less Sugar – How to Cut Down on Sugar – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Decaf-Coffee-–-Is-Decaffeinated-Coffee-Good-or-Bad-–-1.jpg
1415
2120
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:57:572021-03-03 11:01:42Decaf Coffee – Is Decaffeinated Coffee Good or Bad? –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Decaf-Coffee-–-Is-Decaffeinated-Coffee-Good-or-Bad-–-1.jpg
1415
2120
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:57:572021-03-03 11:01:42Decaf Coffee – Is Decaffeinated Coffee Good or Bad? – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-Acidity-–-Everything-You-Need-to-Know-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:52:442021-03-03 11:02:58Coffee Acidity – Everything You Need to Know –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-Acidity-–-Everything-You-Need-to-Know-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:52:442021-03-03 11:02:58Coffee Acidity – Everything You Need to Know – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10-Best-Coffee-Protein-Shakes-–-Make-Your-Morning-Better-–-1.jpg
960
640
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:48:282021-03-03 11:04:1910 Best Coffee Protein Shakes – Make Your Morning Better –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10-Best-Coffee-Protein-Shakes-–-Make-Your-Morning-Better-–-1.jpg
960
640
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:48:282021-03-03 11:04:1910 Best Coffee Protein Shakes – Make Your Morning Better – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/We-Love-Coffee-–-10-Best-Reasons-Why-Coffee-is-Good-For-You-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:43:082021-03-03 11:05:47We Love Coffee – 10 Best Reasons Why Coffee is Good For You –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/We-Love-Coffee-–-10-Best-Reasons-Why-Coffee-is-Good-For-You-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:43:082021-03-03 11:05:47We Love Coffee – 10 Best Reasons Why Coffee is Good For You – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/What-is-Chicory-Coffee-–-A-Healthy-Alternative-to-Coffee-or-Not-–-1-scaled.jpg
1747
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:37:062021-03-03 11:06:59What is Chicory Coffee? – A Healthy Alternative to Coffee or Not –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/What-is-Chicory-Coffee-–-A-Healthy-Alternative-to-Coffee-or-Not-–-1-scaled.jpg
1747
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:37:062021-03-03 11:06:59What is Chicory Coffee? – A Healthy Alternative to Coffee or Not – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10-Best-Natural-Sugar-Substitutes-–-Your-Healthier-Sugar-Alternatives-to-Try-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:32:372021-03-03 11:08:1810 Best Natural Sugar Substitutes – Your Healthier Sugar Alternatives to Try –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10-Best-Natural-Sugar-Substitutes-–-Your-Healthier-Sugar-Alternatives-to-Try-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:32:372021-03-03 11:08:1810 Best Natural Sugar Substitutes – Your Healthier Sugar Alternatives to Try – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Withdrawal-and-Headaches-–-7-Tips-for-Relief-and-More-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:16:582021-03-03 11:12:51Caffeine Withdrawal and Headaches – 7 Tips for Relief and More –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Withdrawal-and-Headaches-–-7-Tips-for-Relief-and-More-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:16:582021-03-03 11:12:51Caffeine Withdrawal and Headaches – 7 Tips for Relief and More – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/20-Best-Ground-Coffee-Recipes-9.jpg
896
640
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:10:502021-03-03 11:14:2220 Best Ground Coffee Recipes – Make Delicious Food With Coffee –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/20-Best-Ground-Coffee-Recipes-9.jpg
896
640
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 07:10:502021-03-03 11:14:2220 Best Ground Coffee Recipes – Make Delicious Food With Coffee – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/15-Great-Coffee-Breakfast-Smoothies-–-Simply-Delicious-Ways-to-Boost-Your-Morning-–14.jpg
1050
700
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 06:52:492021-03-03 11:46:4615 Great Coffee Breakfast Smoothies – Delicious Ways to Boost Your Morning –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/15-Great-Coffee-Breakfast-Smoothies-–-Simply-Delicious-Ways-to-Boost-Your-Morning-–14.jpg
1050
700
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 06:52:492021-03-03 11:46:4615 Great Coffee Breakfast Smoothies – Delicious Ways to Boost Your Morning – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Improves-Exercise-Performance-–-Does-Coffee-Make-Fit-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 05:58:522021-03-03 11:49:58Caffeine Improves Exercise Performance – Does Coffee Make Fit? –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Improves-Exercise-Performance-–-Does-Coffee-Make-Fit-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 05:58:522021-03-03 11:49:58Caffeine Improves Exercise Performance – Does Coffee Make Fit? – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Is-Coffee-Addictive-–-A-Critical-Look-at-Coffee-and-Caffeine-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 05:38:012021-03-03 11:55:00Is Coffee Addictive? – A Critical Look at Coffee and Caffeine –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Is-Coffee-Addictive-–-A-Critical-Look-at-Coffee-and-Caffeine-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 05:38:012021-03-03 11:55:00Is Coffee Addictive? – A Critical Look at Coffee and Caffeine – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-and-Migraines-–-Does-Caffeine-Trigger-or-Treat-Migraines-–-2-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 05:06:562021-03-03 12:03:40Caffeine and Migraines – Does Caffeine Trigger or Treat Migraines –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-and-Migraines-–-Does-Caffeine-Trigger-or-Treat-Migraines-–-2-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 05:06:562021-03-03 12:03:40Caffeine and Migraines – Does Caffeine Trigger or Treat Migraines – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-And-Your-Body-Everything-to-Know-About-Caffeine-Effects-–-2-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:44:592021-03-03 12:09:01Caffeine And Your Body – Everything to Know About Caffeine Effects –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-And-Your-Body-Everything-to-Know-About-Caffeine-Effects-–-2-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:44:592021-03-03 12:09:01Caffeine And Your Body – Everything to Know About Caffeine Effects – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/How-To-Open-A-Coffee-Shop-The-10-Most-Important-Steps-1-scaled.jpg
1708
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:37:232021-03-03 12:10:33How To Open A Coffee Shop – The 10 Most Important Steps
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/How-To-Open-A-Coffee-Shop-The-10-Most-Important-Steps-1-scaled.jpg
1708
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:37:232021-03-03 12:10:33How To Open A Coffee Shop – The 10 Most Important Steps https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/How-To-Sell-Coffee-Online-–-Open-Your-Own-Online-Coffee-Shop-1-scaled.jpg
1697
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:32:292021-03-03 12:12:06How To Sell Coffee Online – Open Your Own Online Coffee Shop
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/How-To-Sell-Coffee-Online-–-Open-Your-Own-Online-Coffee-Shop-1-scaled.jpg
1697
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:32:292021-03-03 12:12:06How To Sell Coffee Online – Open Your Own Online Coffee Shop https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-and-Depression-Does-Caffeine-Help-with-Depression-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:23:222021-03-03 12:13:42Caffeine and Depression – Does Caffeine Help with Depression? –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-and-Depression-Does-Caffeine-Help-with-Depression-–-1-scaled.jpg
1707
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:23:222021-03-03 12:13:42Caffeine and Depression – Does Caffeine Help with Depression? – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/20-Best-Coffee-Dessert-Recipes-–-Your-Perfectly-Delicious-Coffee-Treat-–-1-scaled.jpg
1708
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:13:312021-03-03 12:17:1120 Best Coffee Dessert Recipes – Your Perfectly Delicious Coffee Treat –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/20-Best-Coffee-Dessert-Recipes-–-Your-Perfectly-Delicious-Coffee-Treat-–-1-scaled.jpg
1708
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 04:13:312021-03-03 12:17:1120 Best Coffee Dessert Recipes – Your Perfectly Delicious Coffee Treat – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-and-Caffeine-–-How-Much-Caffeine-is-Okay-for-You-–-1-scaled.jpg
1709
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 03:54:492021-03-03 12:25:58Coffee and Caffeine – How Much Caffeine is Okay for You? –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-and-Caffeine-–-How-Much-Caffeine-is-Okay-for-You-–-1-scaled.jpg
1709
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 03:54:492021-03-03 12:25:58Coffee and Caffeine – How Much Caffeine is Okay for You? – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Make-Your-Coffee-Better-–-6-Fun-Ways-to-Boost-Your-Coffee-–-1-scaled.jpg
1709
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 03:45:112021-03-03 12:29:07Make Your Coffee Better – 6 Fun Ways to Boost Your Coffee –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Make-Your-Coffee-Better-–-6-Fun-Ways-to-Boost-Your-Coffee-–-1-scaled.jpg
1709
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 03:45:112021-03-03 12:29:07Make Your Coffee Better – 6 Fun Ways to Boost Your Coffee – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Eating-Coffee-Beans-–-Yummy-Healthy-or-Stupid-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 03:04:352021-03-03 12:37:32Eating Coffee Beans – Yummy, Healthy or Stupid –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Eating-Coffee-Beans-–-Yummy-Healthy-or-Stupid-–-1.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 03:04:352021-03-03 12:37:32Eating Coffee Beans – Yummy, Healthy or Stupid – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Side-Effects-–-10-Side-Effects-of-Too-Much-Caffeine-–-1.jpg
1414
2119
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 02:58:352021-03-03 12:39:16Caffeine Side Effects – 10 Side Effects of Too Much Caffeine –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Caffeine-Side-Effects-–-10-Side-Effects-of-Too-Much-Caffeine-–-1.jpg
1414
2119
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 02:58:352021-03-03 12:39:16Caffeine Side Effects – 10 Side Effects of Too Much Caffeine – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/A-Coffee-Journey-–-10-Steps-From-the-Seed-to-Your-Cup-–-1-scaled.jpg
1700
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 02:31:102021-02-20 14:09:30A Coffee Journey – 10 Steps From the Seed to Your Cup –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/A-Coffee-Journey-–-10-Steps-From-the-Seed-to-Your-Cup-–-1-scaled.jpg
1700
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 02:31:102021-02-20 14:09:30A Coffee Journey – 10 Steps From the Seed to Your Cup – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-Diet-–-Can-You-Really-Lose-Weight-With-Coffee-–-1-2-scaled.jpg
1708
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 02:07:232021-03-03 13:38:57Coffee Diet – Can You Really Lose Weight With Coffee? –
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/Coffee-Diet-–-Can-You-Really-Lose-Weight-With-Coffee-–-1-2-scaled.jpg
1708
2560
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2021-02-12 02:07:232021-03-03 13:38:57Coffee Diet – Can You Really Lose Weight With Coffee? – https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10_reasons_to_drink_coffee_every_day.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2019-11-05 07:26:292021-03-03 13:31:5310 Reasons to Drink Coffee Every Day
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/10_reasons_to_drink_coffee_every_day.jpg
1414
2121
Siamhillscoffee
https://www.siamhillscoffee.com/wp-content/uploads/coffee-logo.png
Siamhillscoffee2019-11-05 07:26:292021-03-03 13:31:5310 Reasons to Drink Coffee Every Day


